What is Medicare?
Medicare is a National Health Insurance Program for:
- People 65 years of age and older.
- Certain persons with disabilities under the age of 65.
- People with end stage renal disease (permanent kidney failure requiring dialysis or a kidney transplant)
Medicare Coverage Options
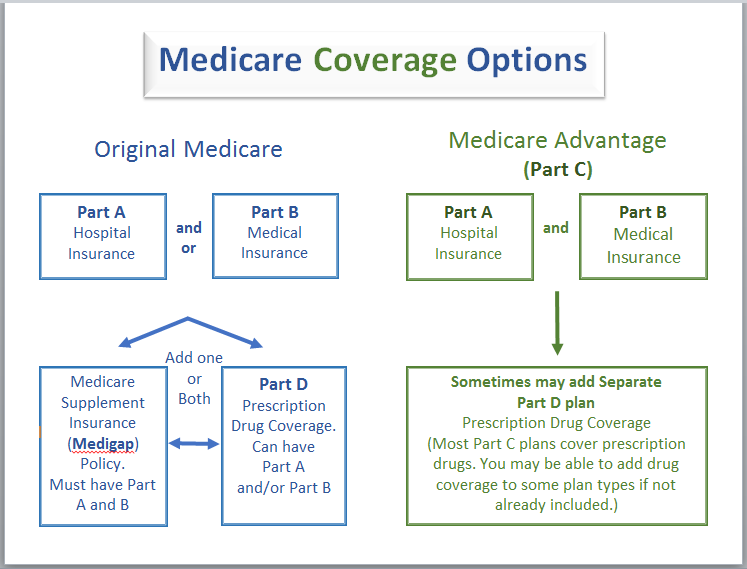
Original Medicare
Medicare will pay for care that is medically "reasonable and necessary" for the treatment of an illness or injury. Medicare does not pay for services that are "routine or custodial" or inpatient care that can be provided by persons without professional skills/training.
Original Medicare is a fee-for-service plan managed by the Federal Government:
- Use your red, white, and blue Medicare card when you receive health care
- Go to any doctor or supplier that accepts Medicare and is accepting new Medicare patients, or to any hospital or other facility
- Pay a set amount for your health care, a deductible, before Medicare pays its part. Then, Medicare pays its share and you pay your share, your coinsurance or copayment, for covered services and supplies.
- You may have a Medigap policy or other supplemental coverage that may pay deductibles, coinsurance, or other costs that aren't covered by Original Medicare.
Medicare is not an entitlement program and should not be confused with Medicaid. The income and assets of a Medicare applicant are not a consideration in determining eligibility or benefit payment.
Medicare has four components, Part A, Part B Part C and Part D
Part A covers inpatient hospital care, hospice care, inpatient care in a skilled nursing facility, and home health care services. Individuals have either paid into Medicare over the course of their employment and automatically become enrolled at age 65, or, if they have been a legal resident for five years or more, they can buy into Medicare.
Part B covers medical care and services provided by doctors and other medical practitioners, durable medical equipment, some outpatient care and home health care services. Individuals choose to become enrolled in Part B when they become eligible for Medicare and pay a monthly premium for that enrollment. If you don't sign up for part b when you are first eligible, you may have to pay a late penalty.
Part C or Medicare Advantage (MA) plans are health plan options that are part of the Medicare program. If you join one of these plans, you generally get all your Medicare-covered health care through that plan which can include prescription drug coverage. Medicare Advantage plans include: Health Maintenance Organization (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPO), Private fee-for-service plans and special needs plans.
Part D covers some prescription drug expenses. Part D is available to any Medicare beneficiary who has Medicare Part A or Part B or both. Part D drug plans are sold by private companies. There is a monthly premium, an annual deductible & co-payments for each prescription and costs vary from plan to plan. Enrollment in Part D is optional. But if you do not sign up when you are first eligible & change your mind later on, you may have to pay a penalty of a higher premium. However, there are some exceptions to the penalty.
"Extra Help" for Medicare beneficiaries may be available for those with limited income & assets to help pay part or all of the costs.
There is a Medicare Annual Enrollment period however, there are exceptions. If you first become eligible for Medicare, you can enroll into a Medicare Part D (Prescription Drug Plan) the first day you become eligible for Part A or Part B. You can also enroll in a Medicare D when you first become eligible for low income subsidy.
Medigap (Medicare Supplemental Plans)
A Medigap policy is health insurance sold by private insurance companies to fill the "gaps" in Original Medicare Plan coverage. Medigap policies help pay some of the health care costs that the Original Medicare Plan doesn't cover. If you are in the Original Medicare Plan and have a Medigap policy, then Medicare and your Medigap policy will pay both their shares of covered health care costs.
Insurance companies can only sell you a "standardized" Medigap policy. These Medigap policies must all have specific benefits so you can compare them easily. You may be able to choose up to 10 different standardized Medigap policies (Medigap Plans A through N). Medigap policies must follow Federal and State laws. These laws protect you. A Medigap policy must be clearly identified on the cover as "Medicare Supplement Insurance." Each plan, A through N, has a different set of basic and extra benefits. It's important to compare Medigap policies because costs can vary. The core benefits in any Medigap Plan A through N are the same for any insurance company. Each insurance company decides which Medigap policies it wants to sell.
Generally, when you buy a Medigap policy you must have Medicare Part A and Part B. You will have to pay the monthly Medicare Part B premium. In addition, you will have to pay a premium to the Medigap insurance company.
You and your spouse must each buy separate Medigap policies. Your Medigap policy won't cover any health care costs for your spouse.
To learn more about Medigap (Medicare Supplemental Insurance) visit the State of CT Insurance Department Here
For more information on Medicare click here.




